Myopia
Myopia, or nearsightedness, is now recognized as one of the most pressing public health challenges in eye care. Primary eye care professionals are often the first line of defense in detecting, managing, and educating patients about the risks associated with progressive myopia—including retinal detachment, myopic macular degeneration (MMD), and glaucoma.
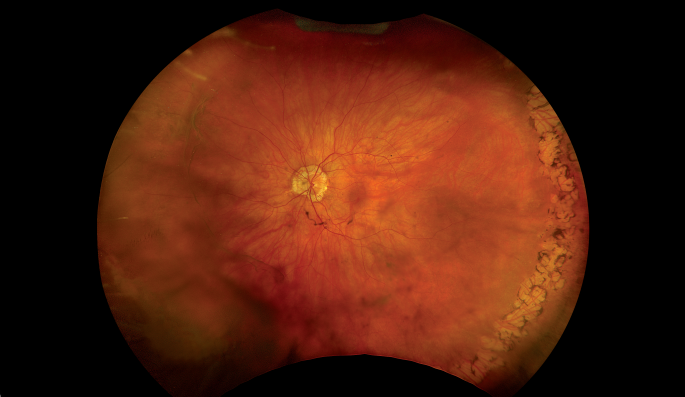
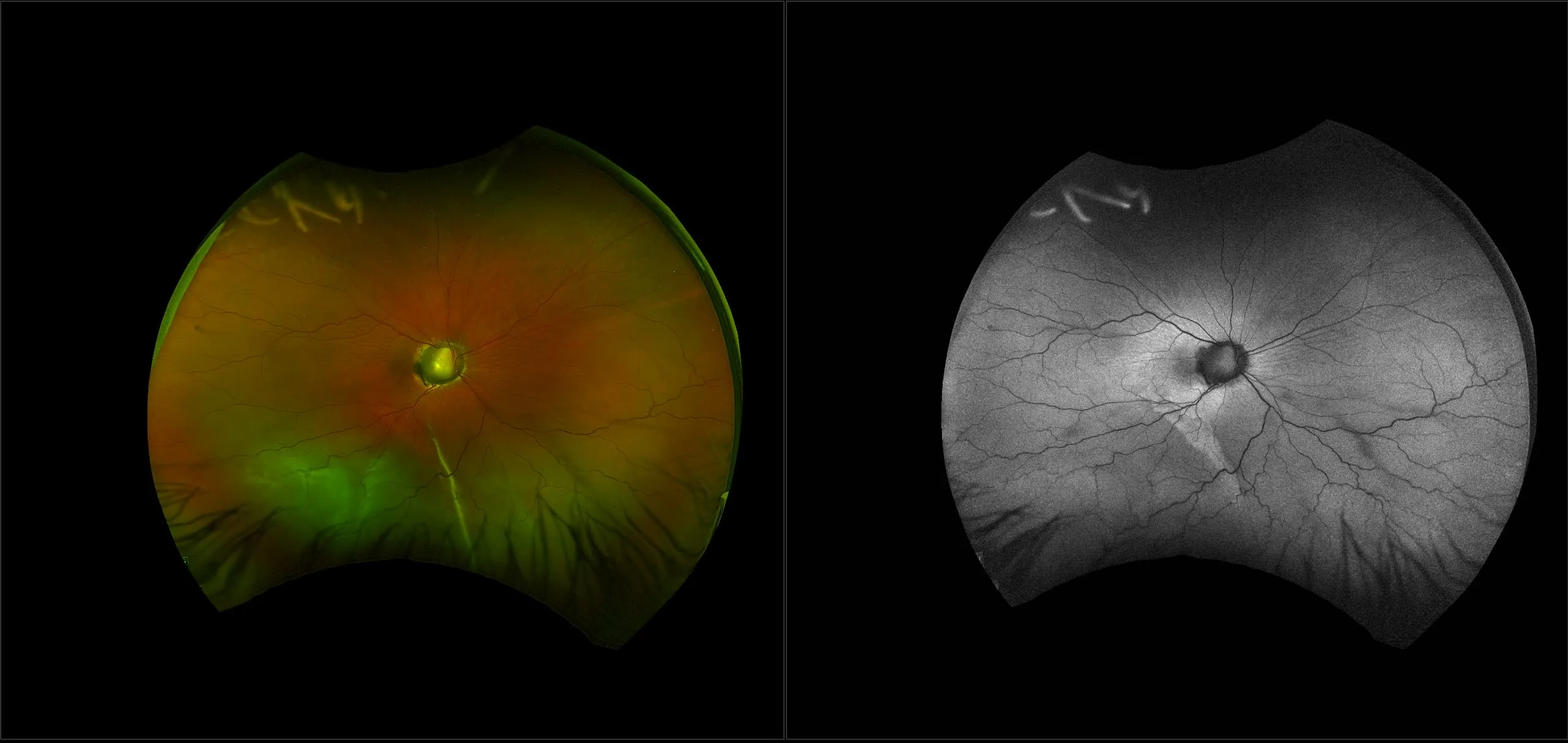
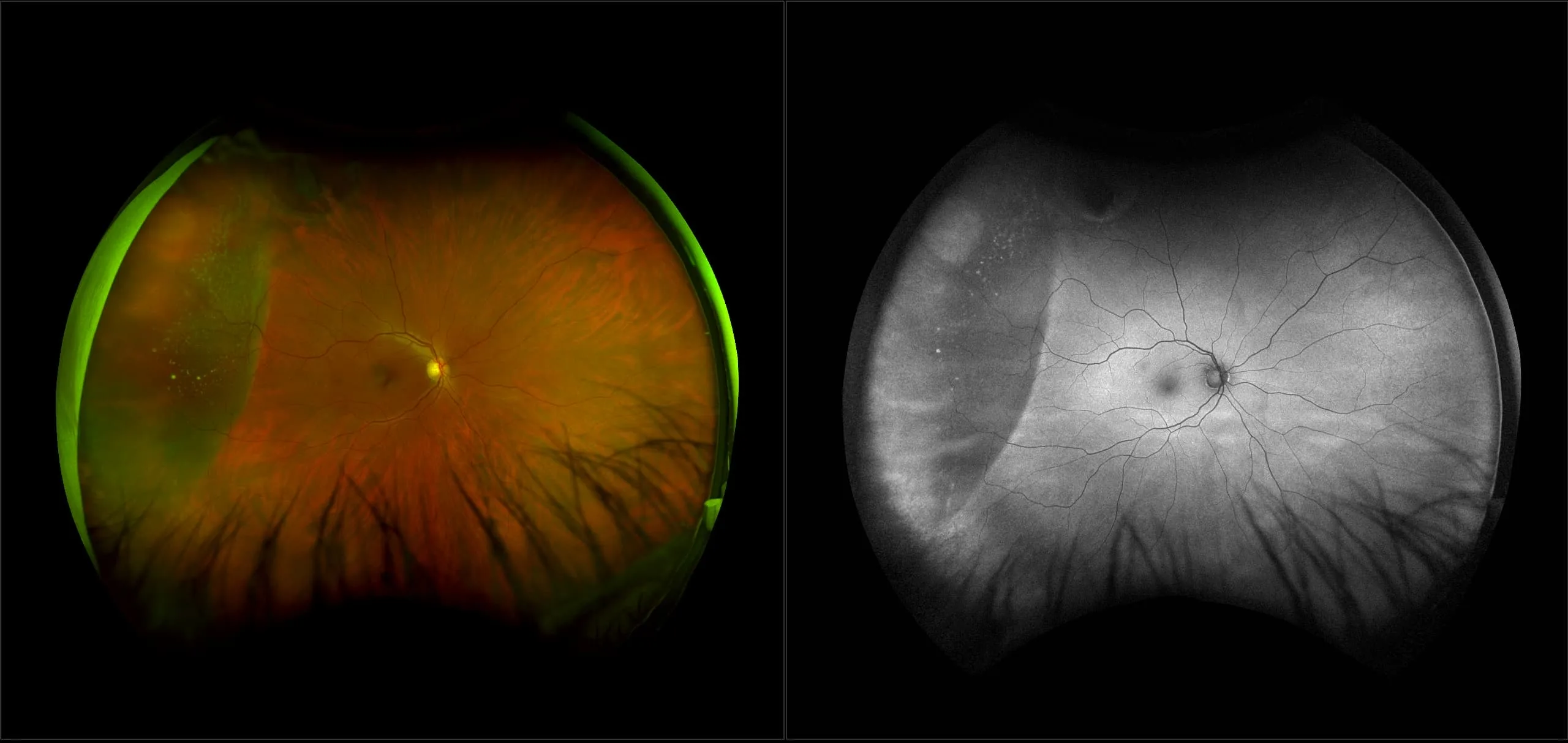
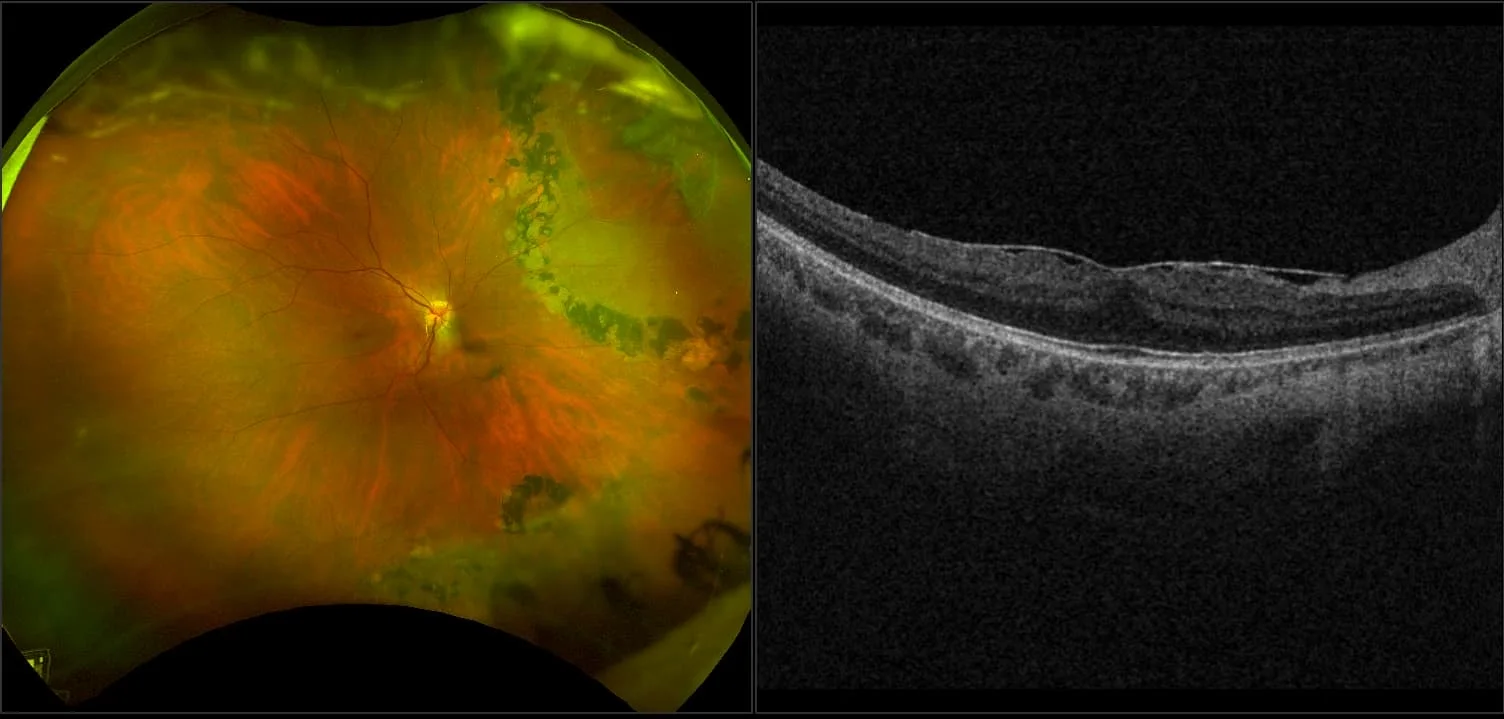
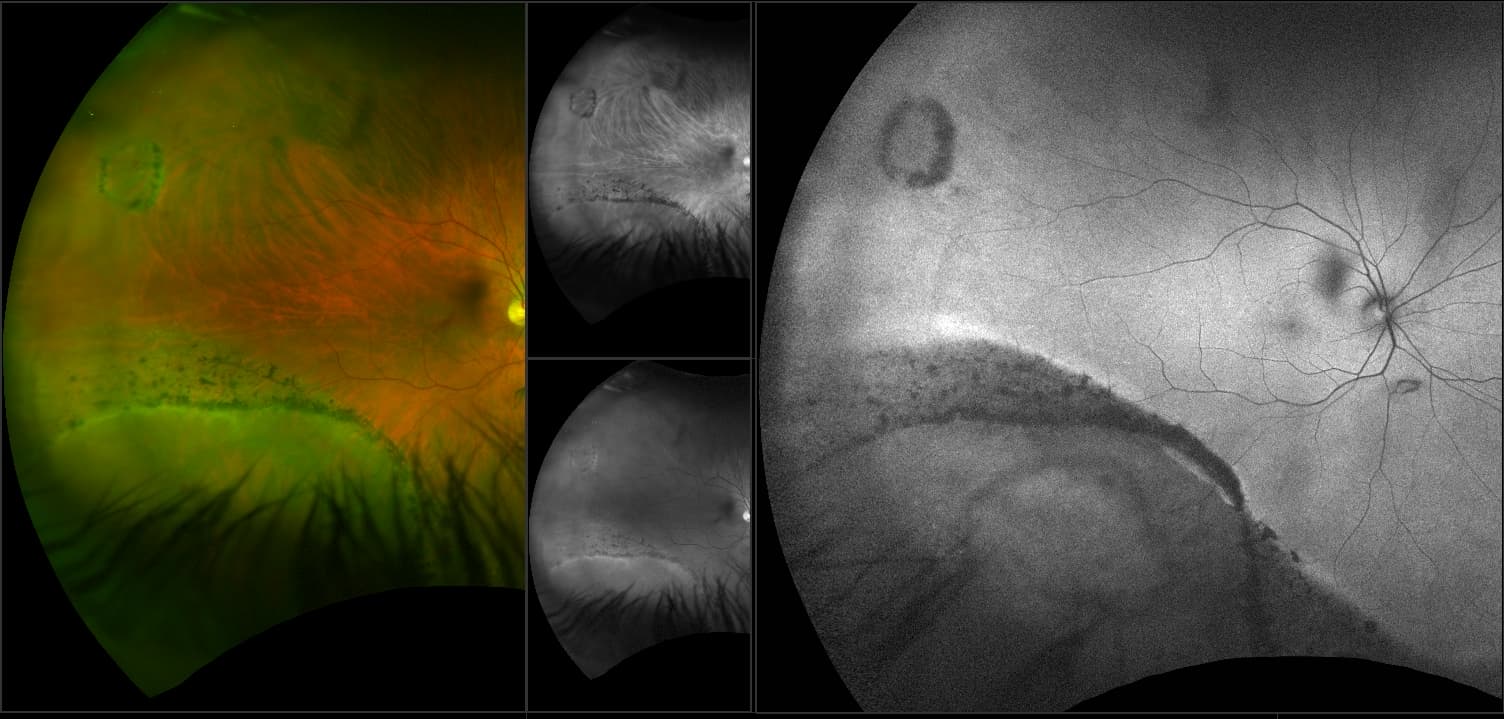
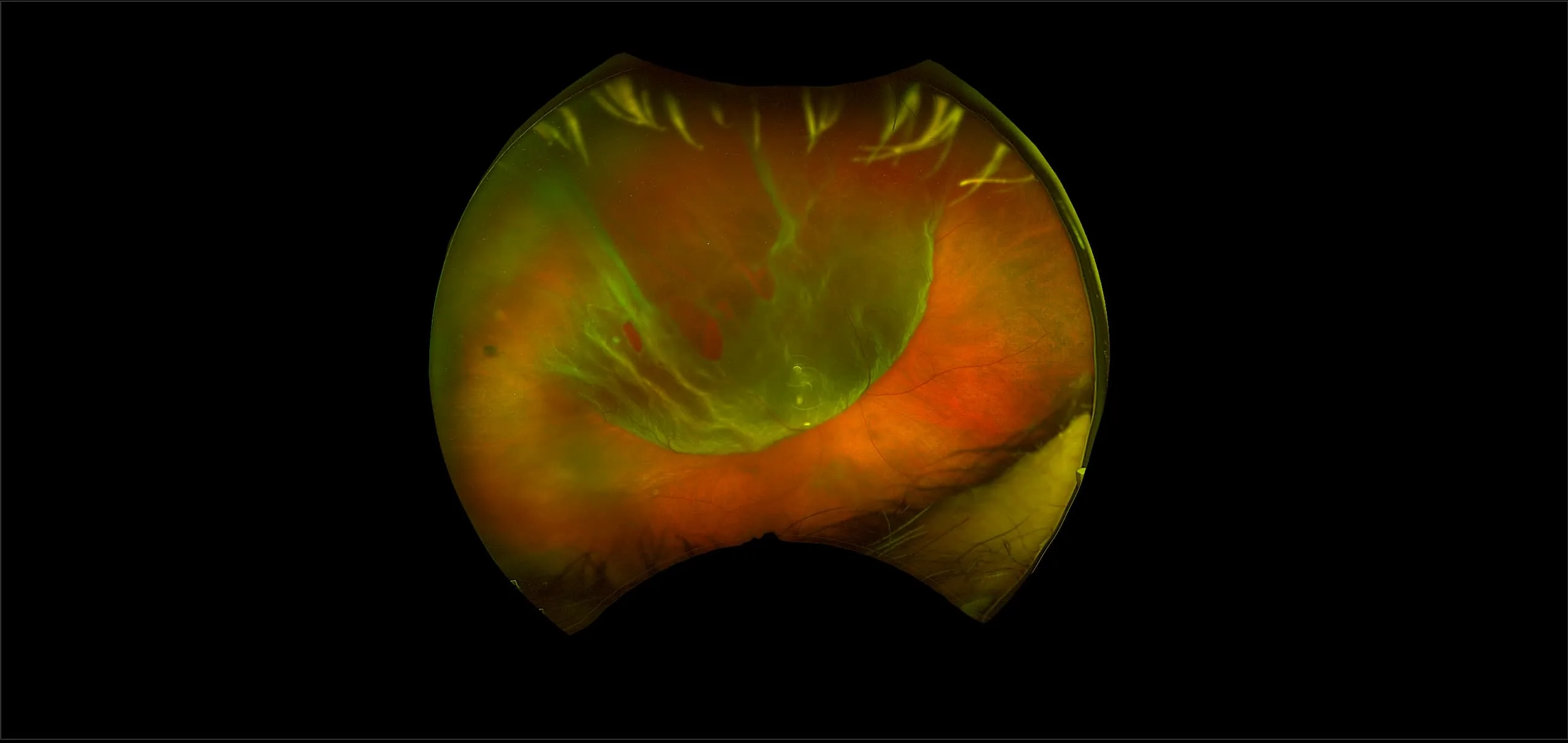
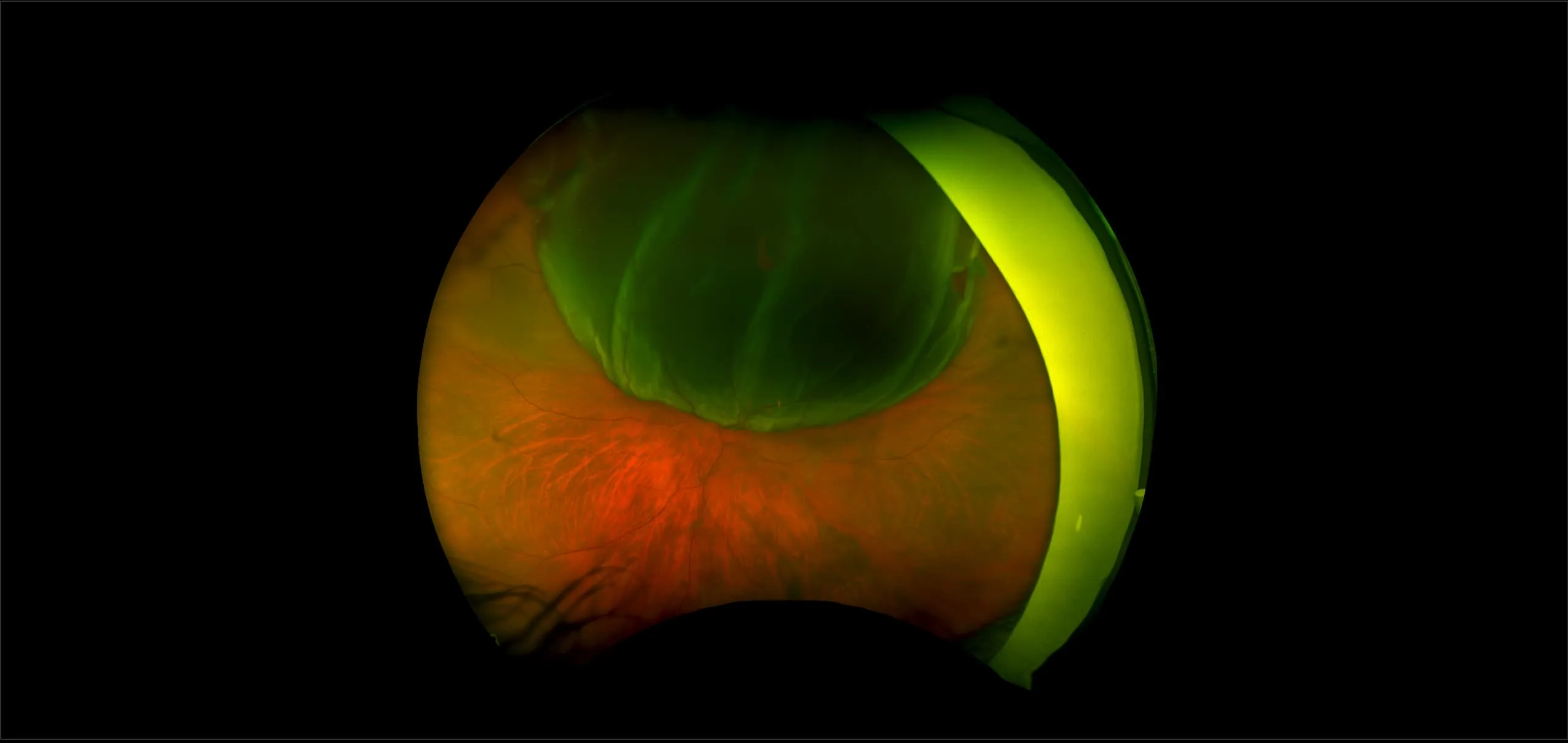
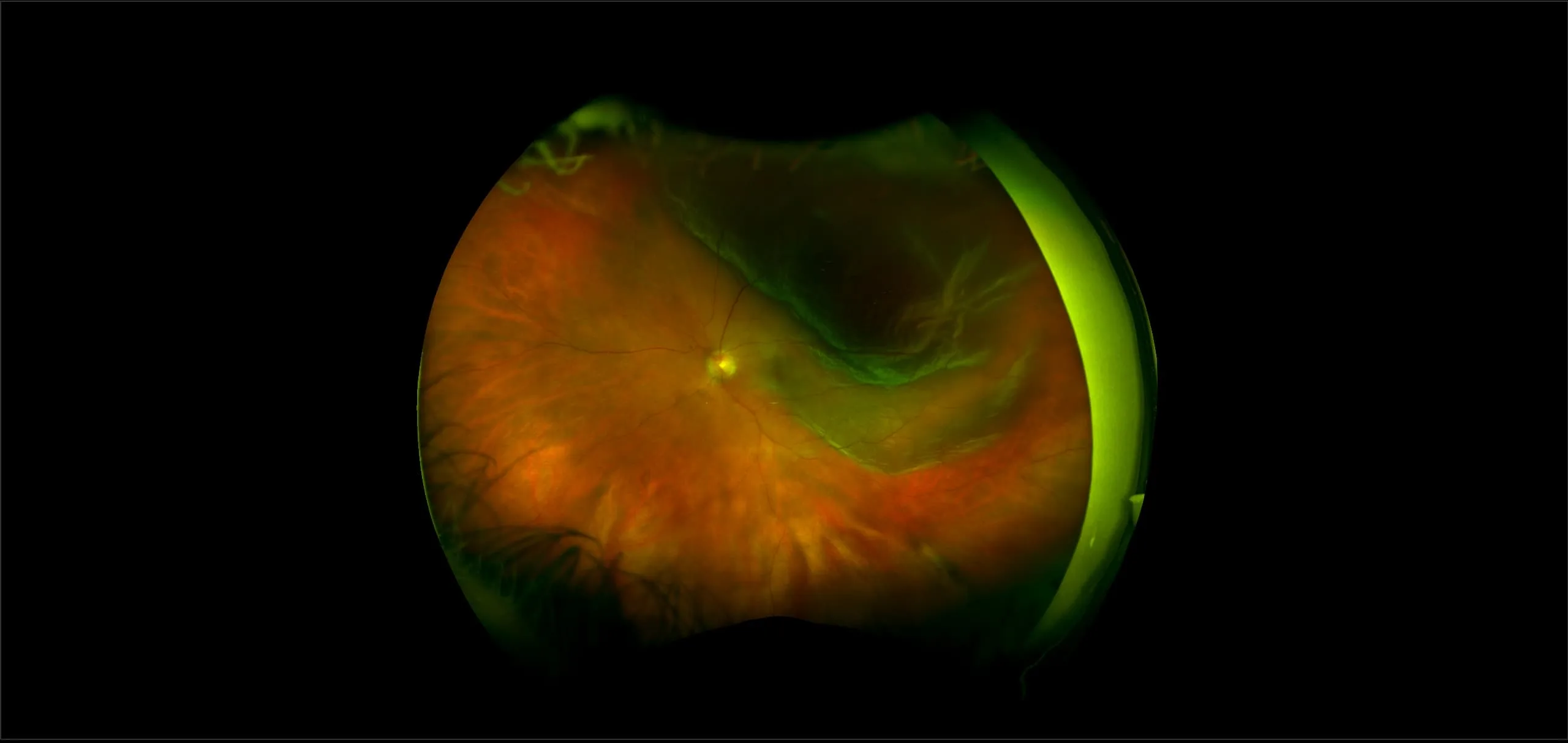
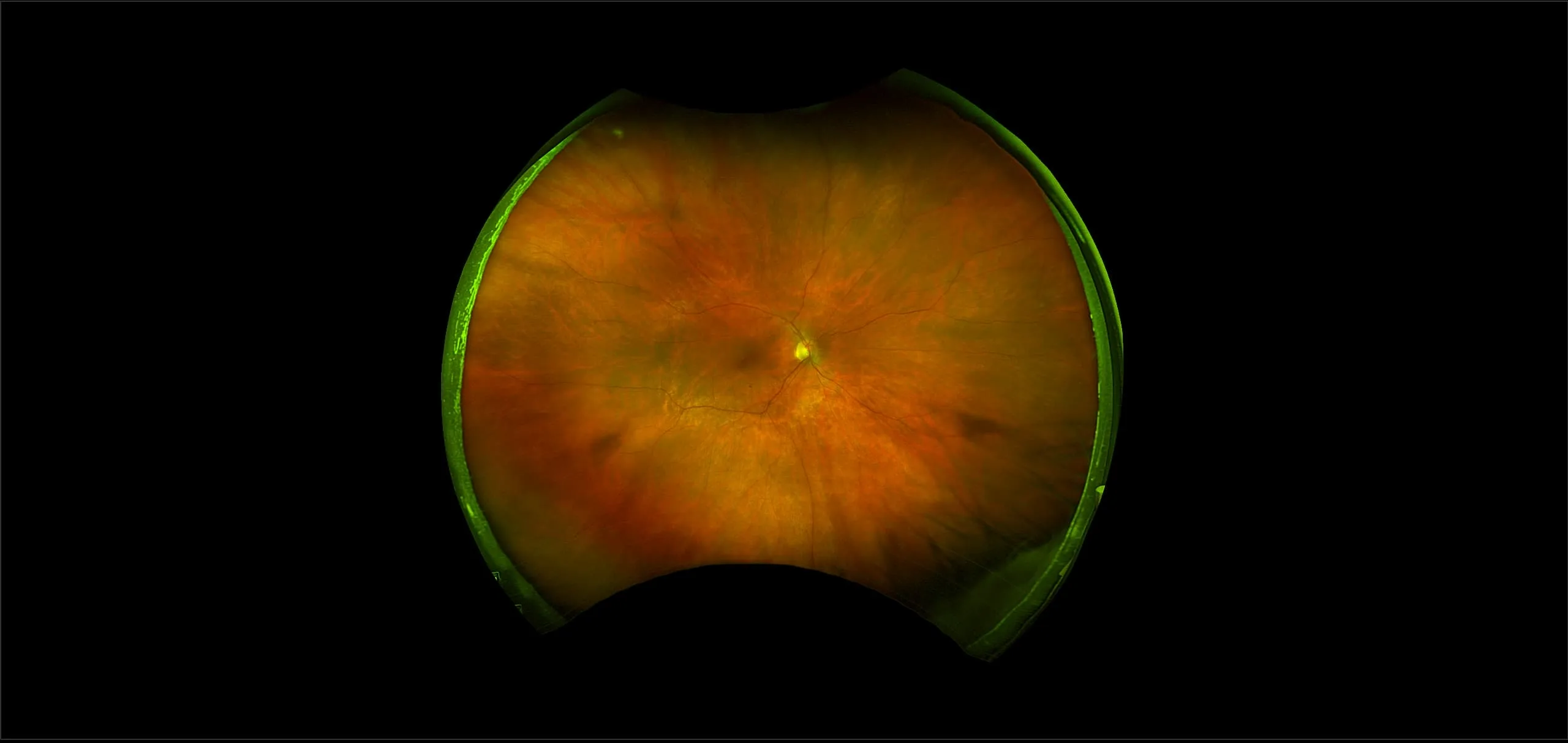
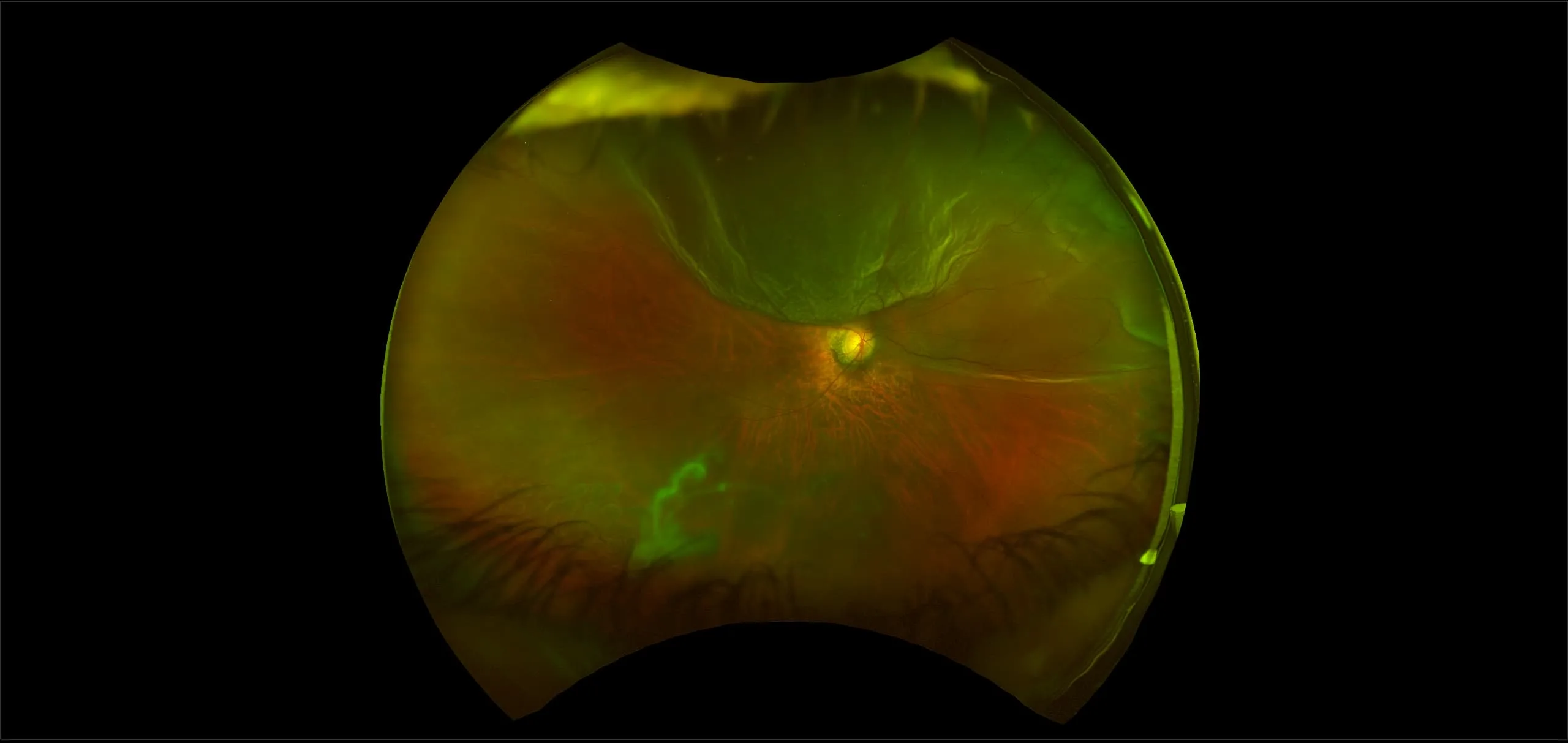
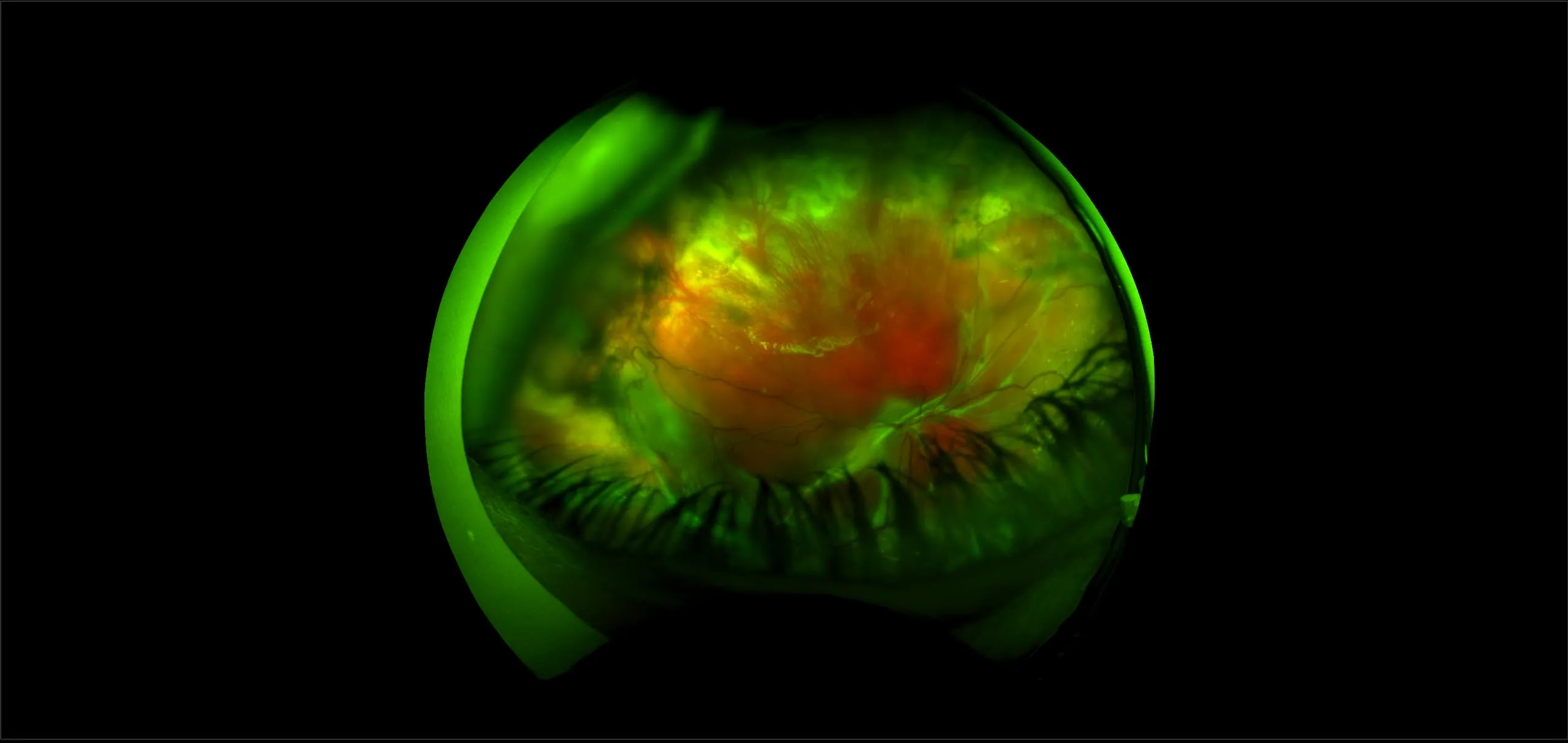
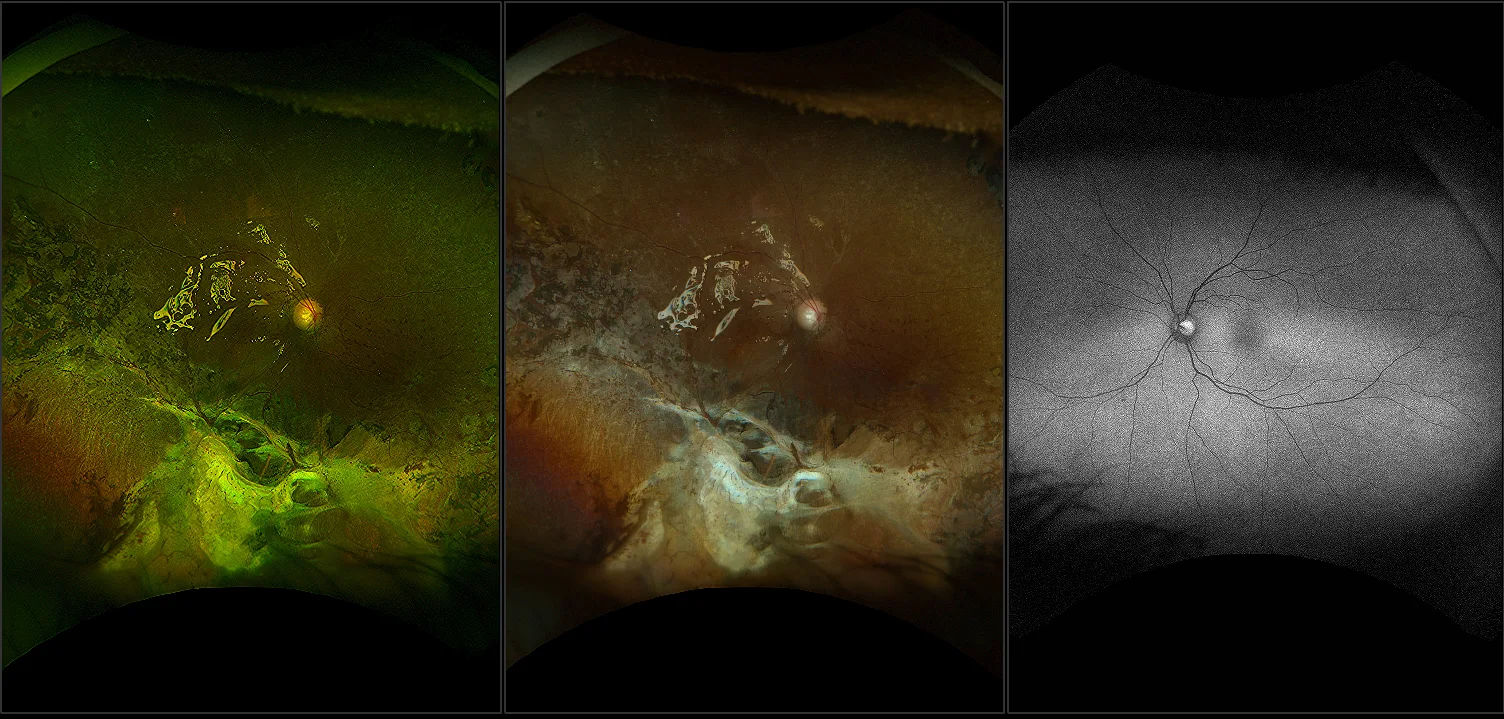
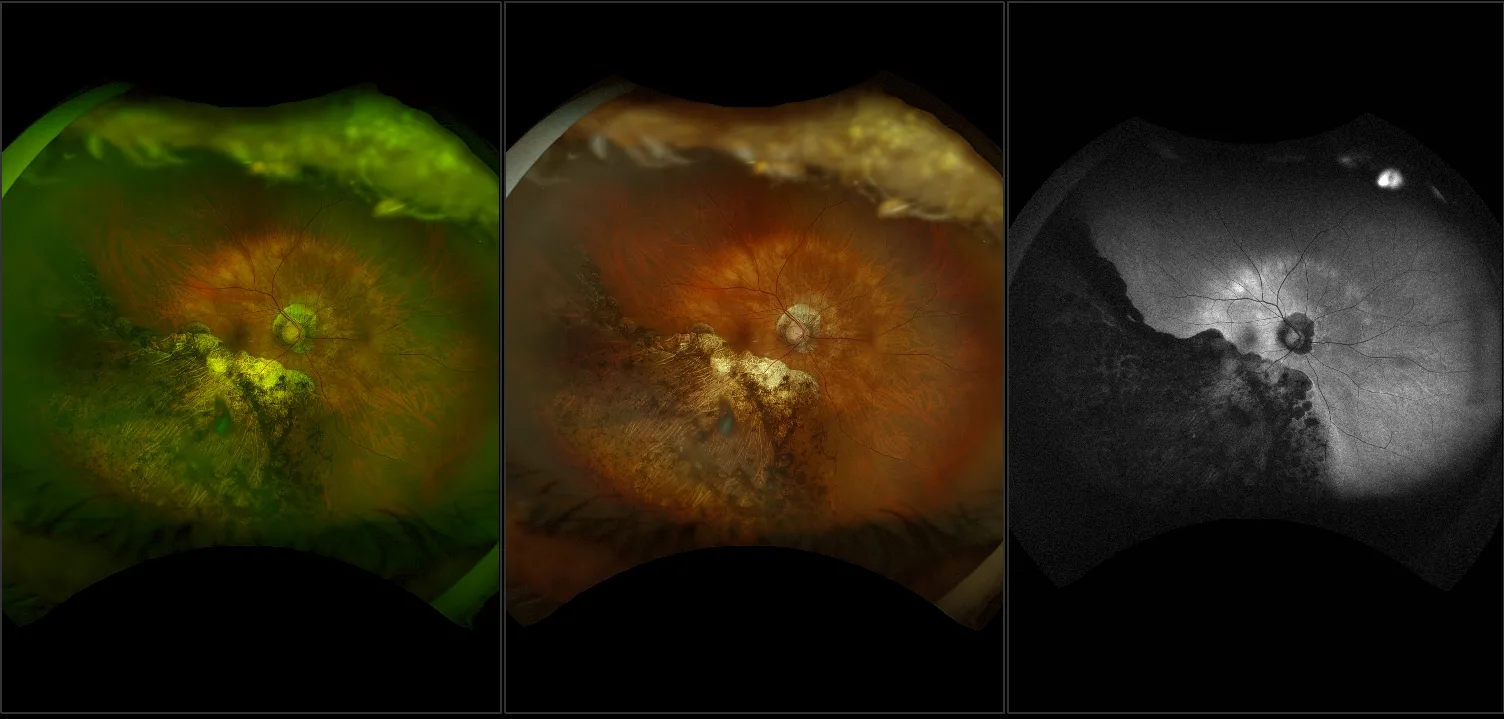
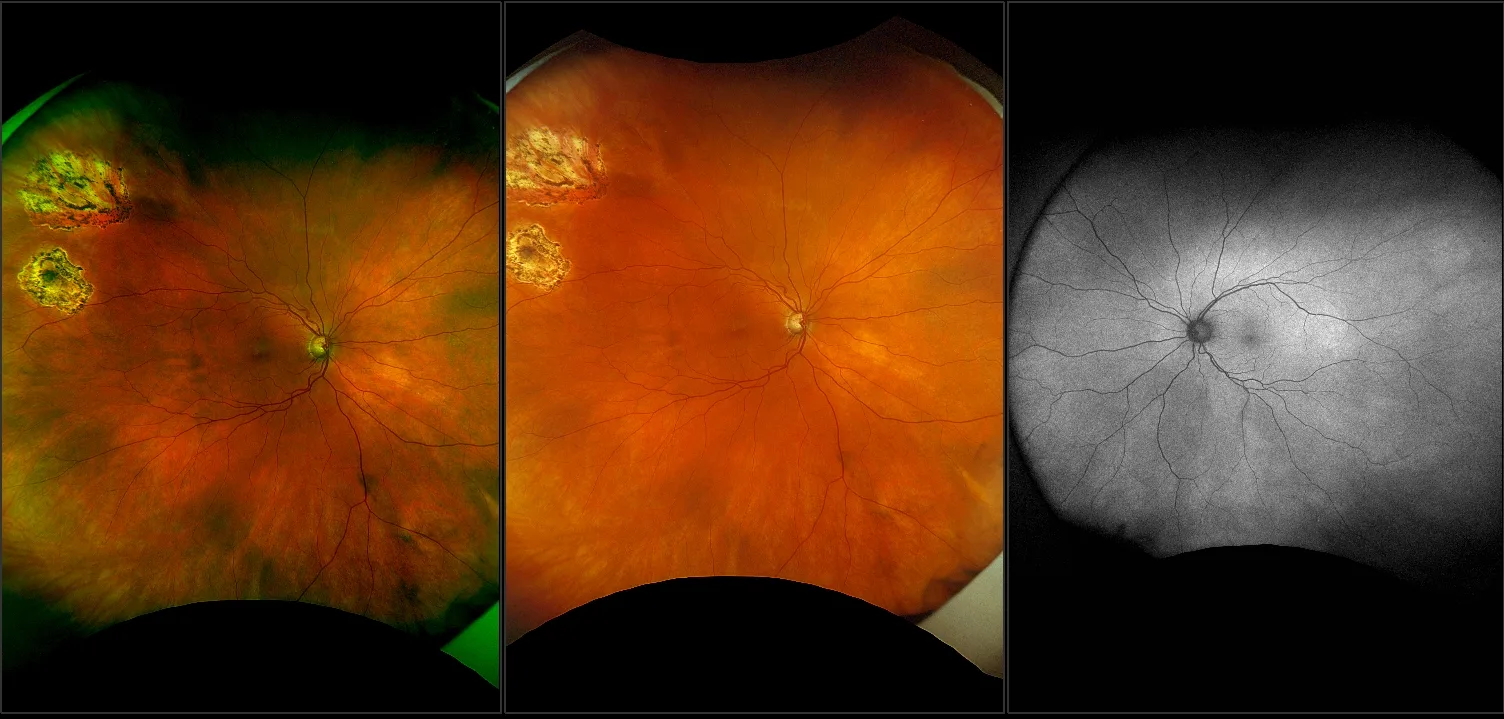
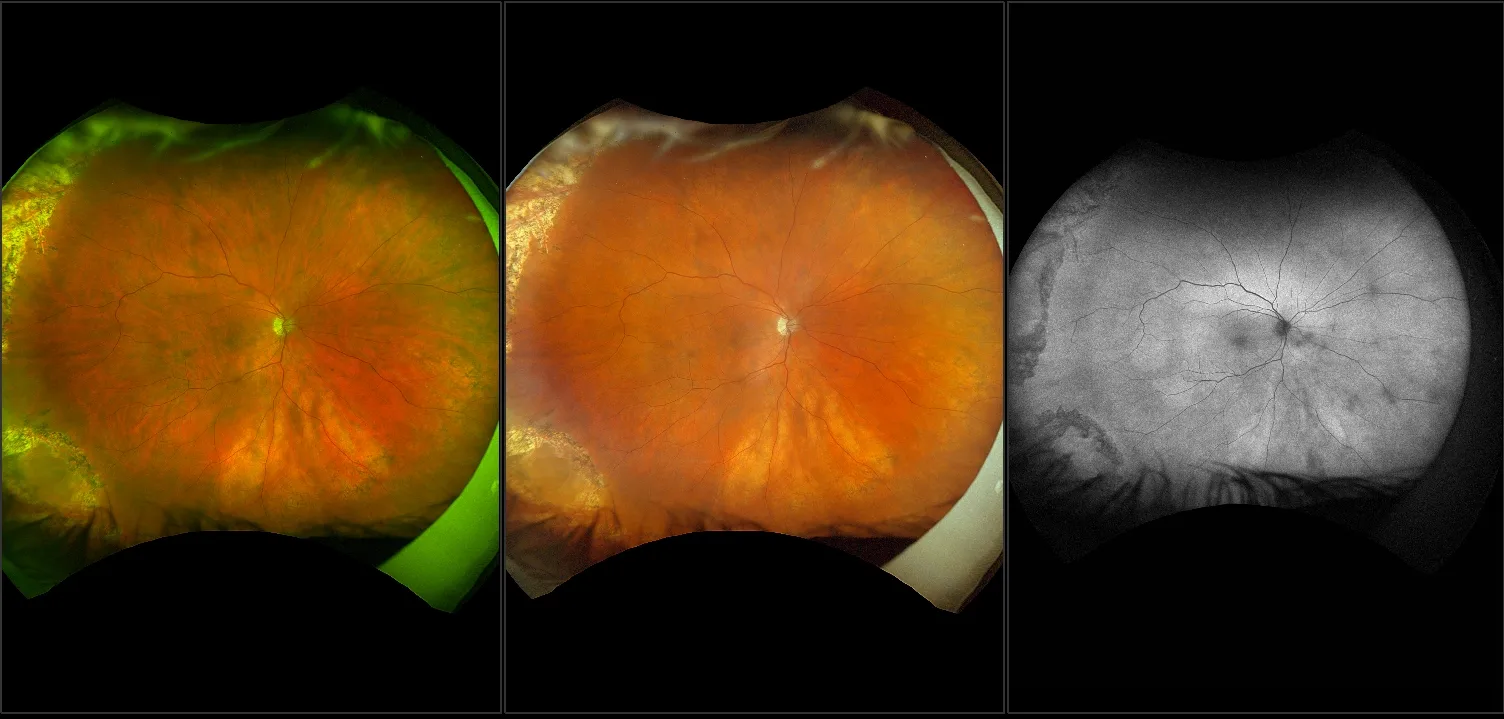
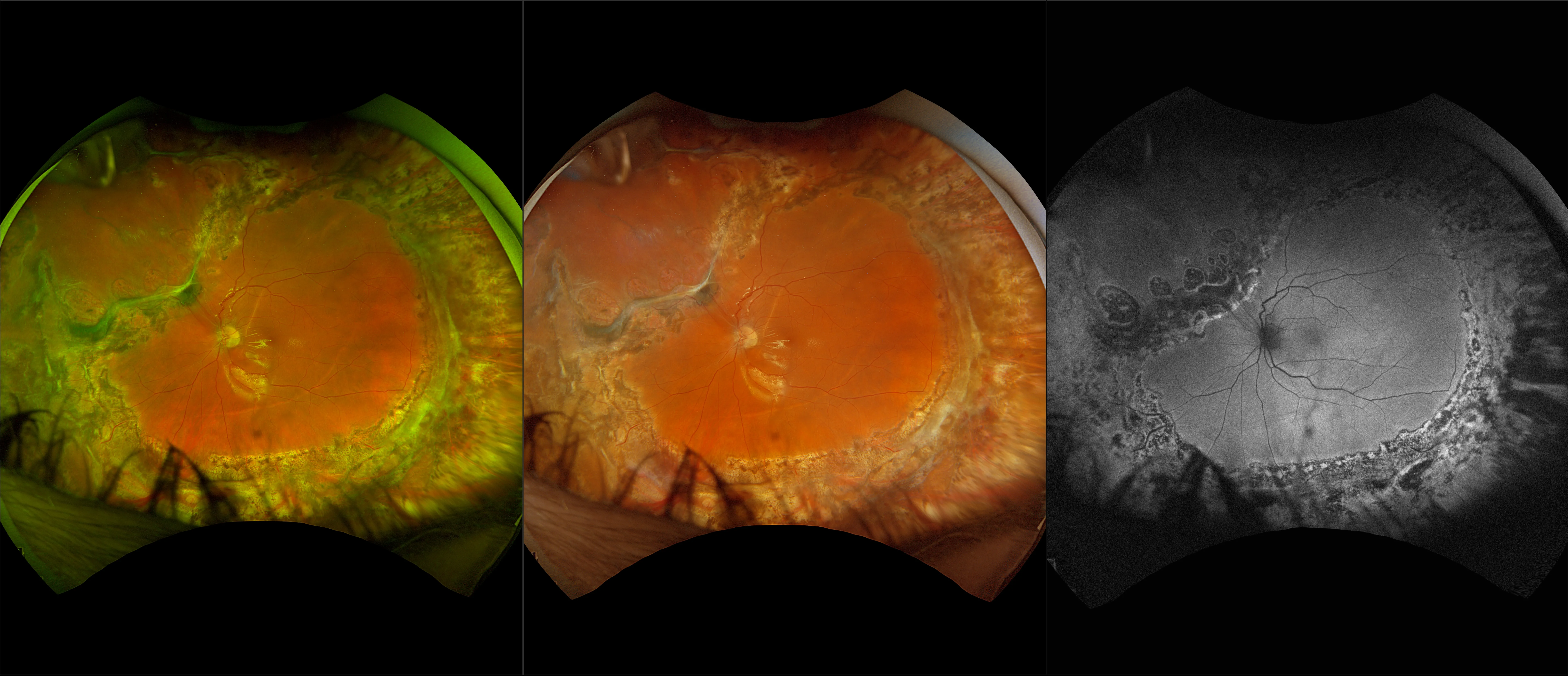
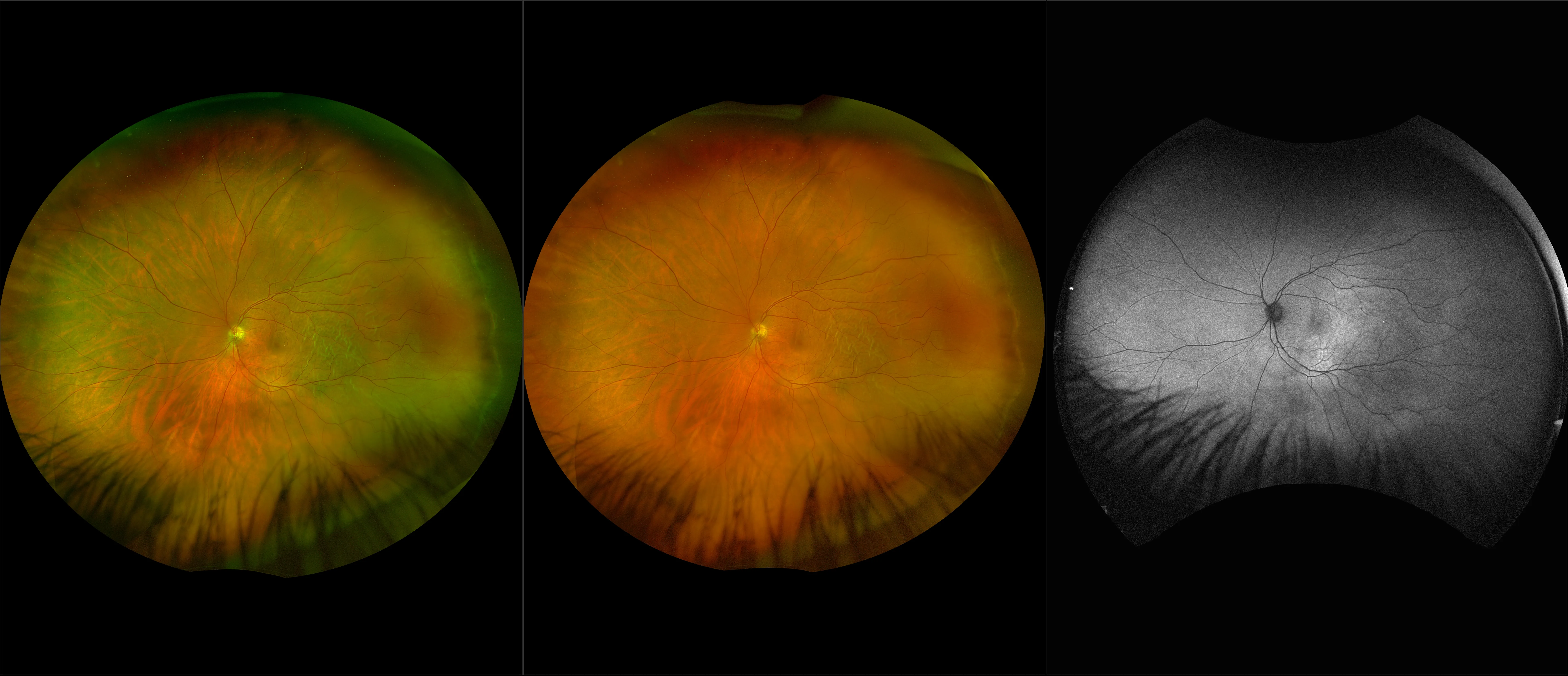
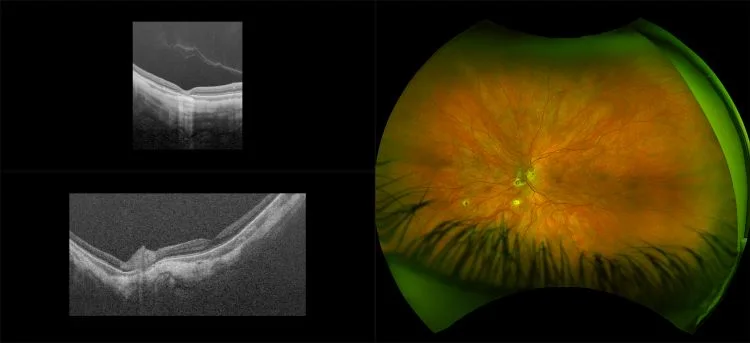
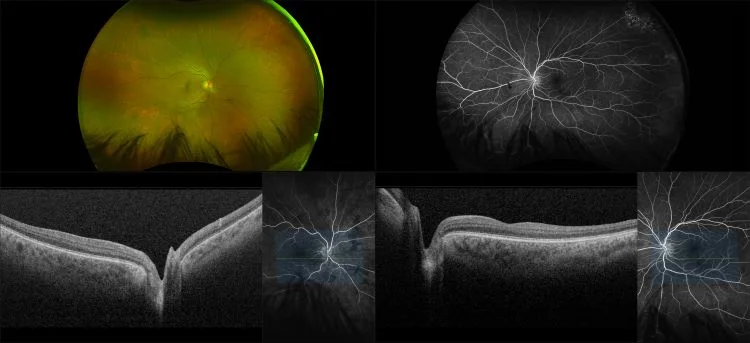
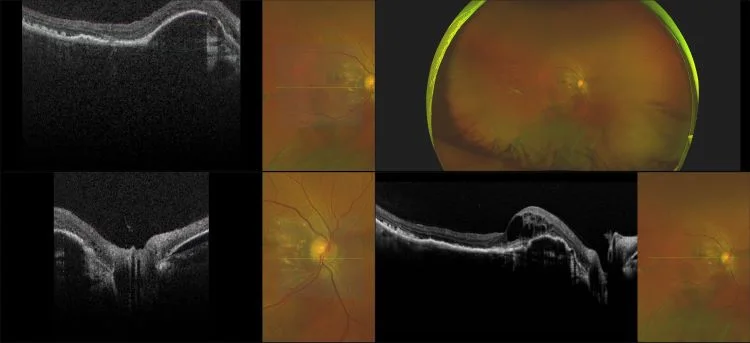
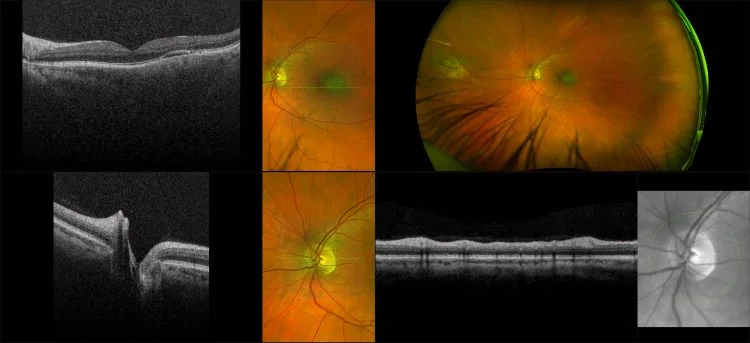
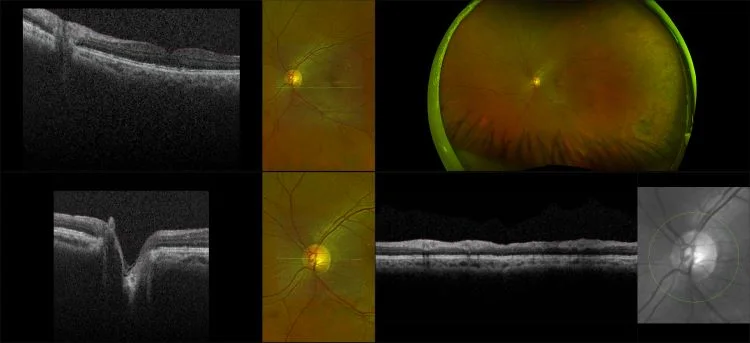
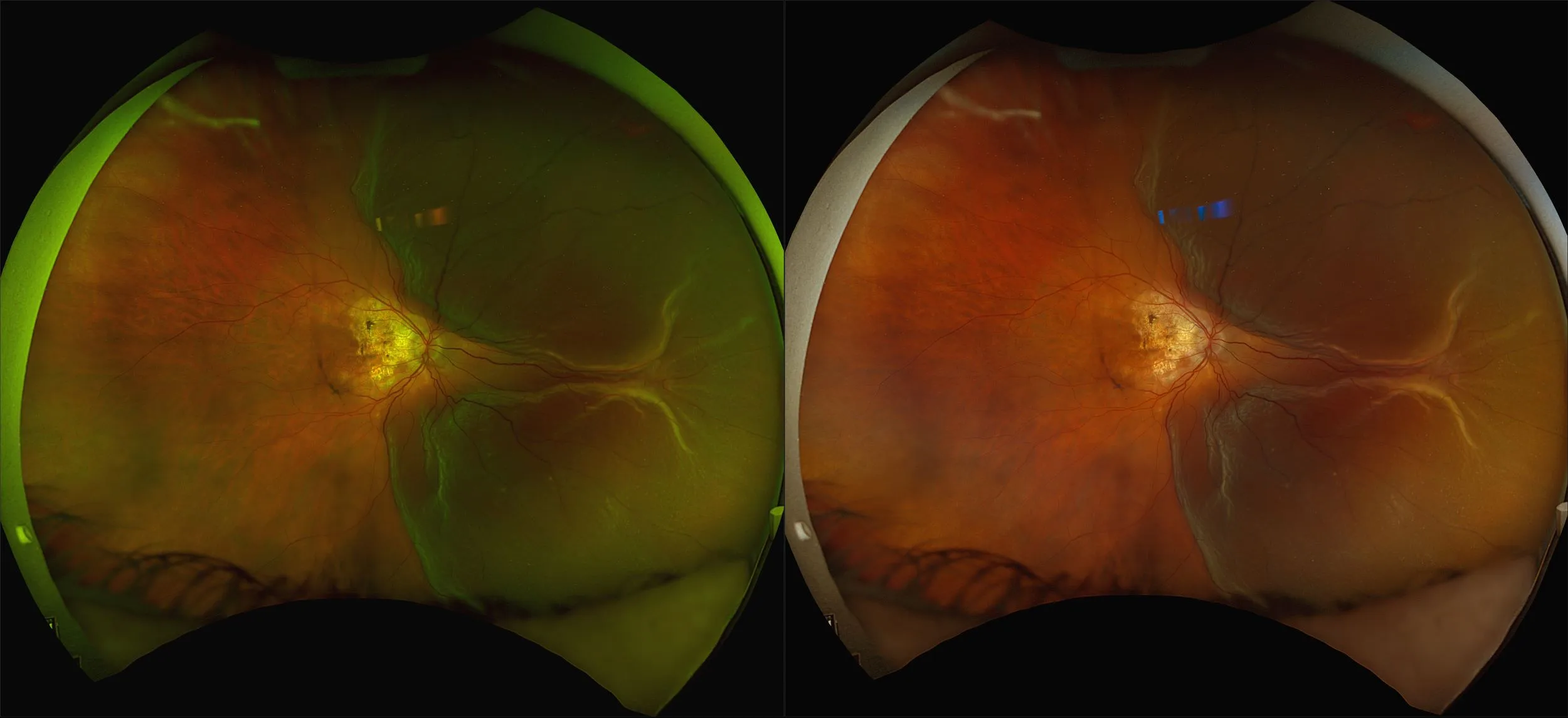
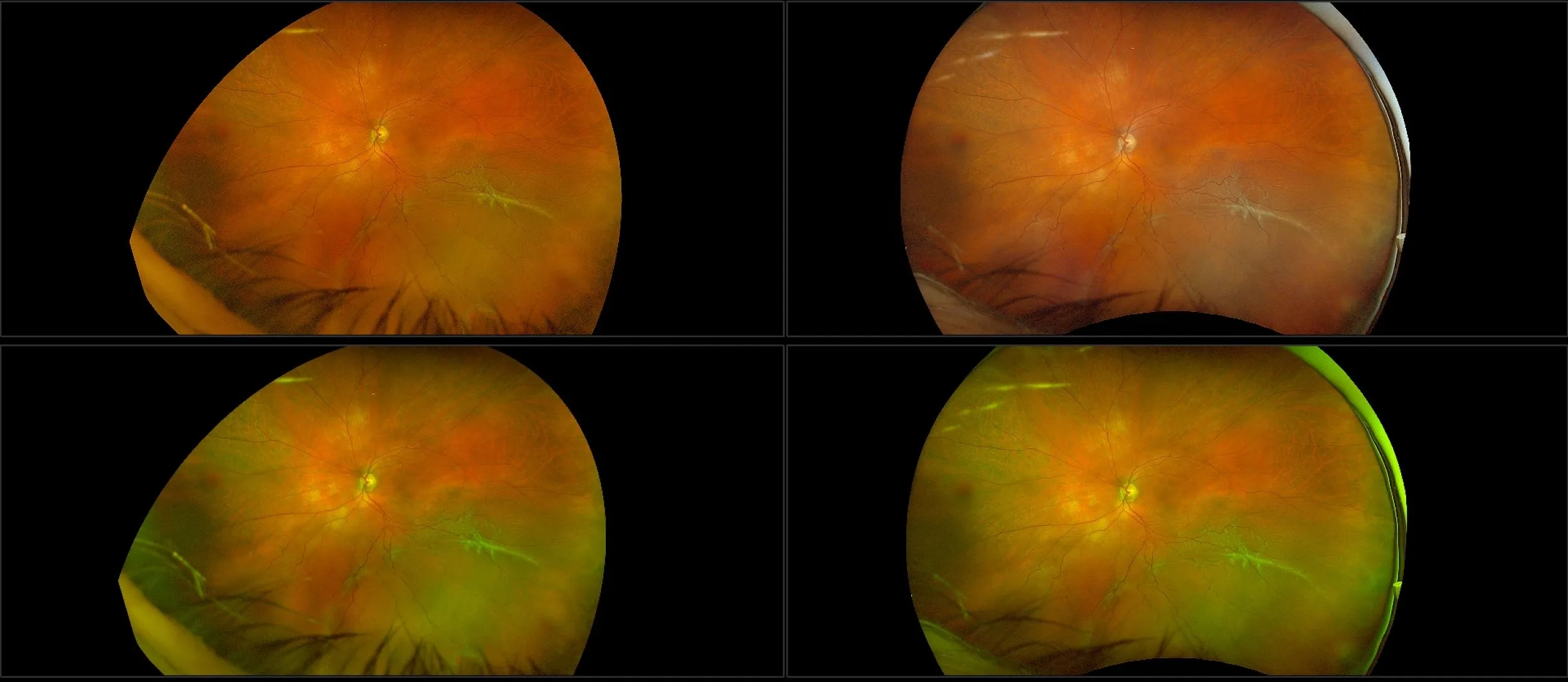
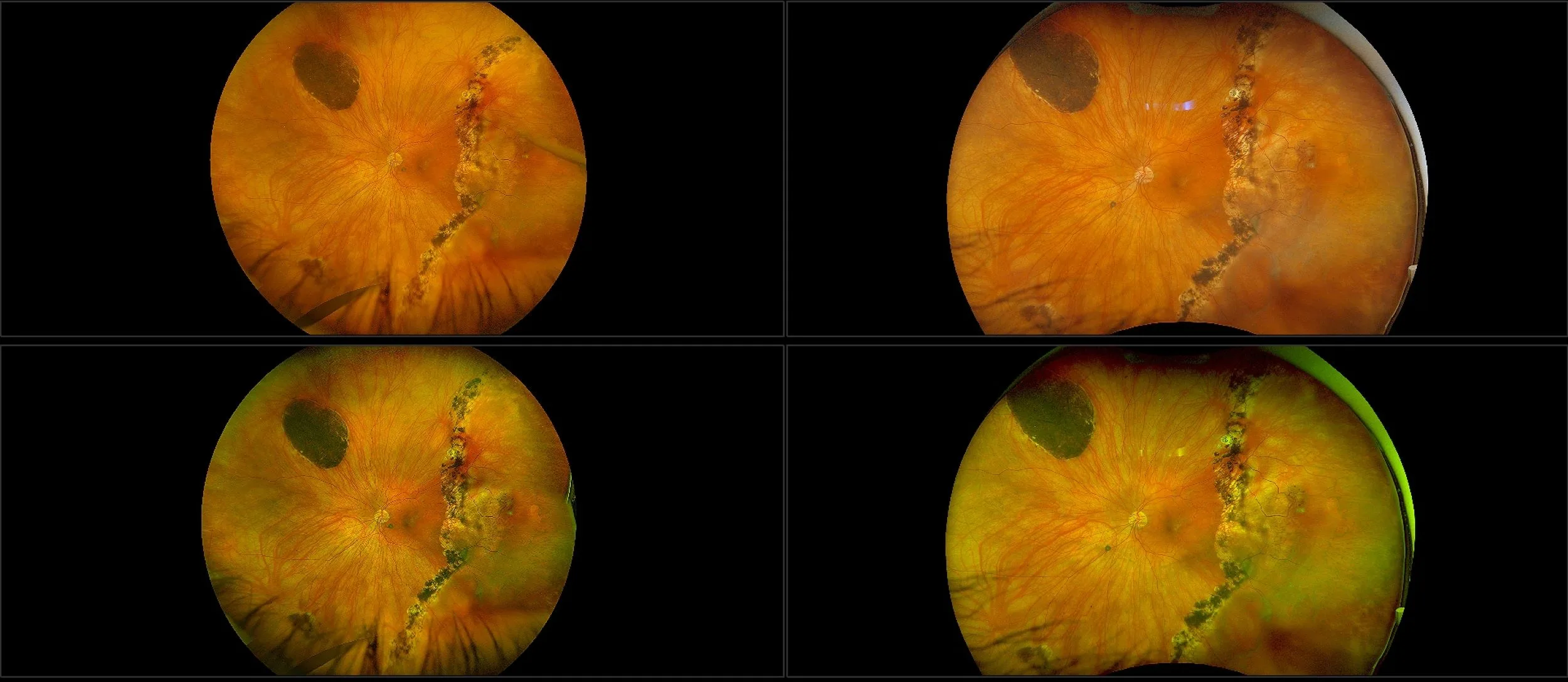
Myopia-related pathology often originates or extends into the retinal periphery, which is why optomap ultra-widefield retinal imaging, with up to 200° in a single image assists eye care professionals to detect peripheral changes like lattice degeneration, paving the way for timely referrals and preventative care.
Studies have demonstrated that UWF imaging in combination with BIO improves sensitivity of retinal lesions by 30% than traditional ophthalmoscopy alone.
As the front line in the fight against the myopia epidemic, primary eye care providers need tools that match the challenge - Optos ultra-widefield and OCT technology may be the correct tool for meeting that challenge for myopic patients.
Clinical Studies
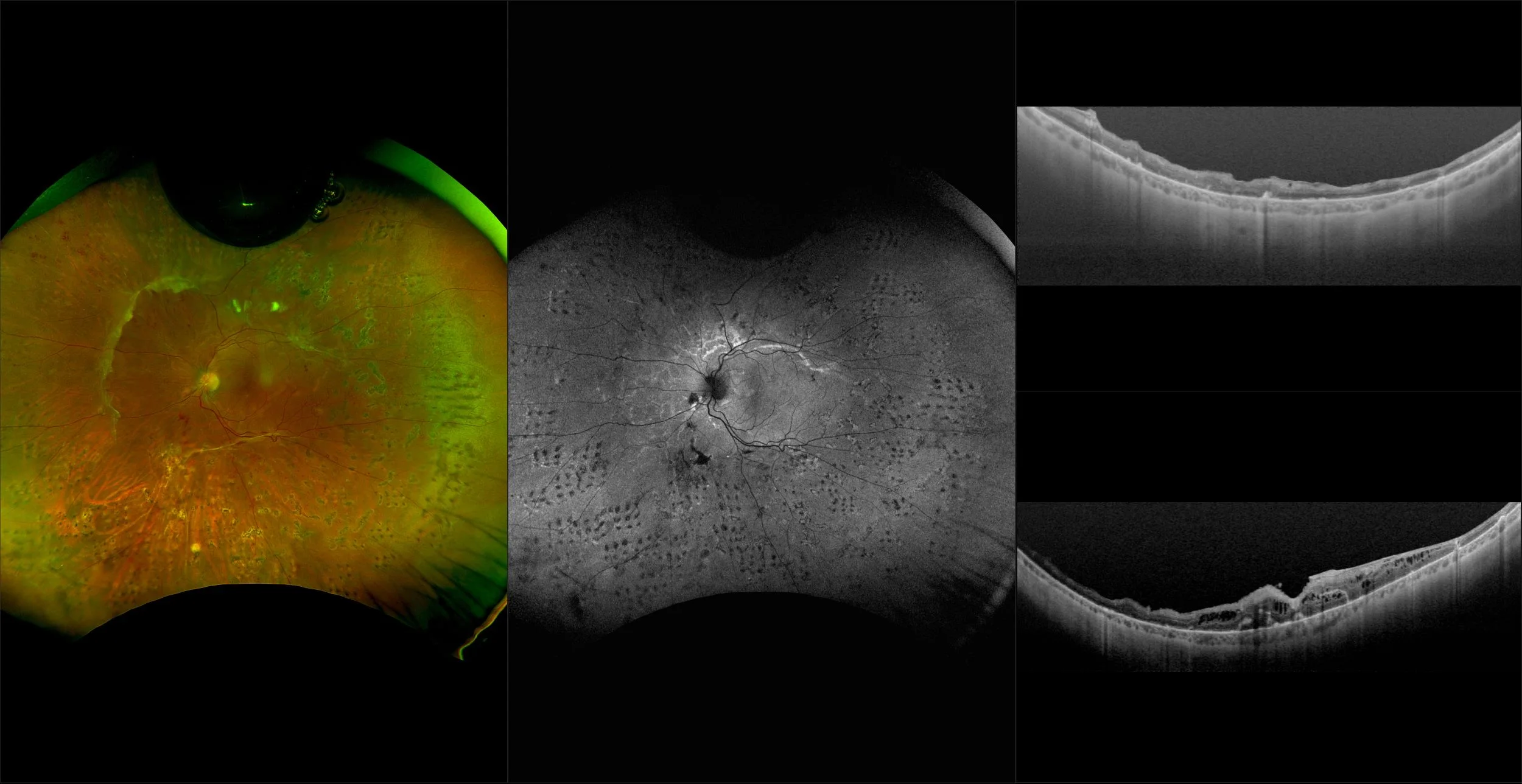
Morphology and incidence of drusen-like deposits in peripheral retina of eyes with high myopia
Determining the morphology and incidence of peripheral drusen-like deposits in eyes with pathological myopia using UWF fundus photographs and UWF OCT images.
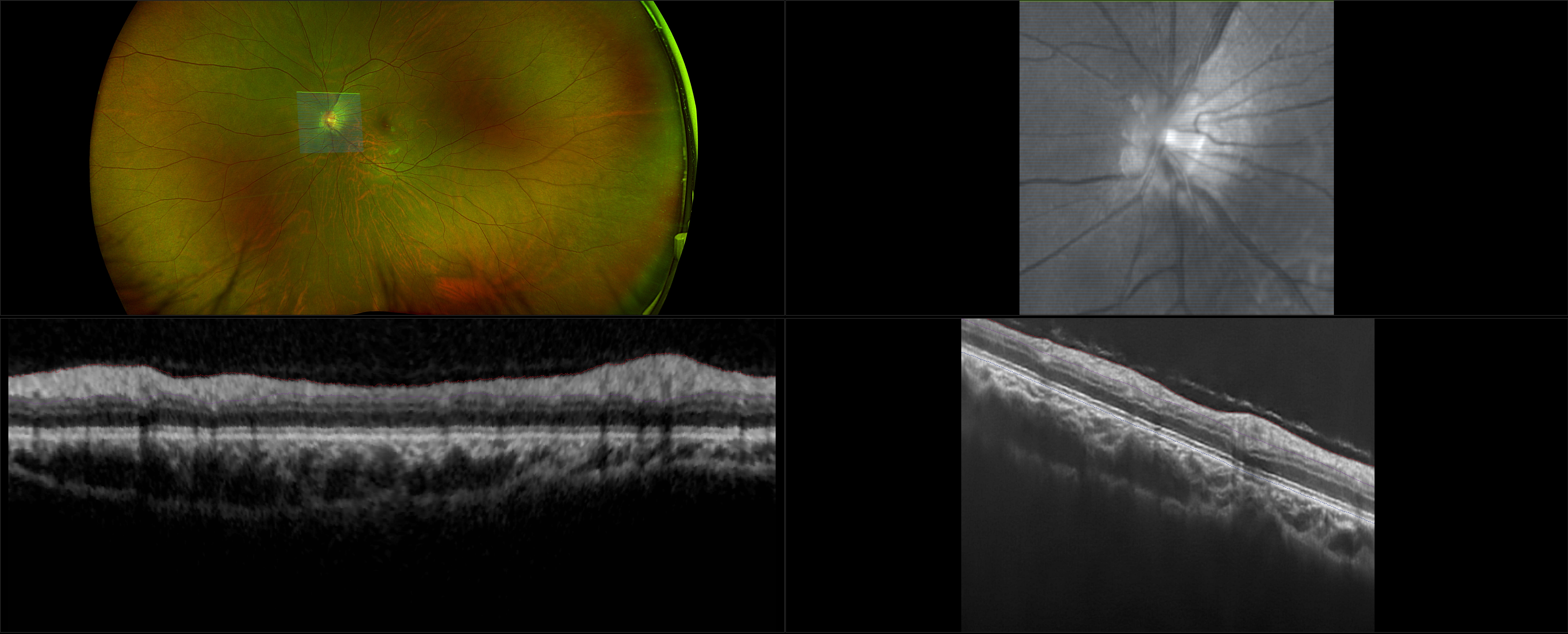
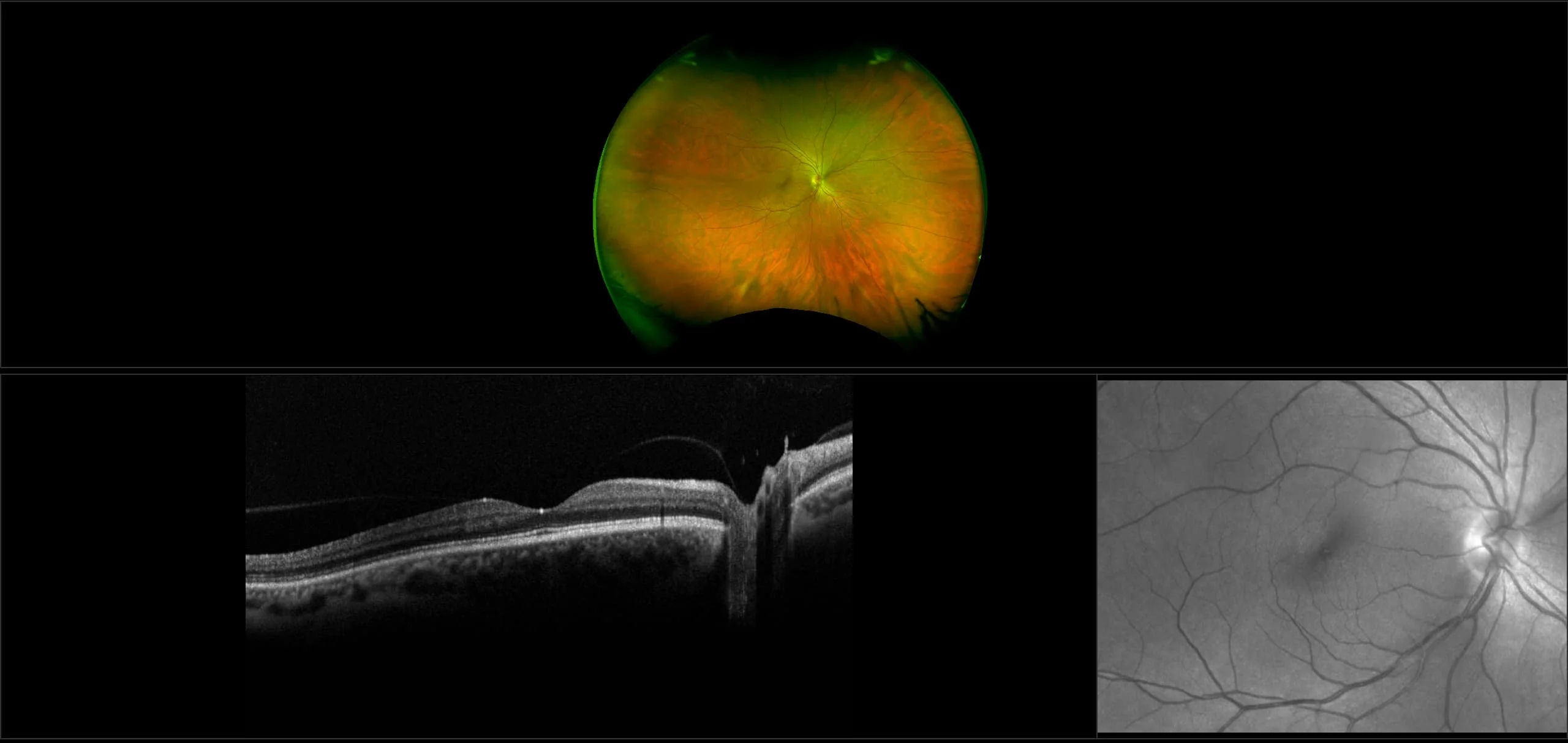
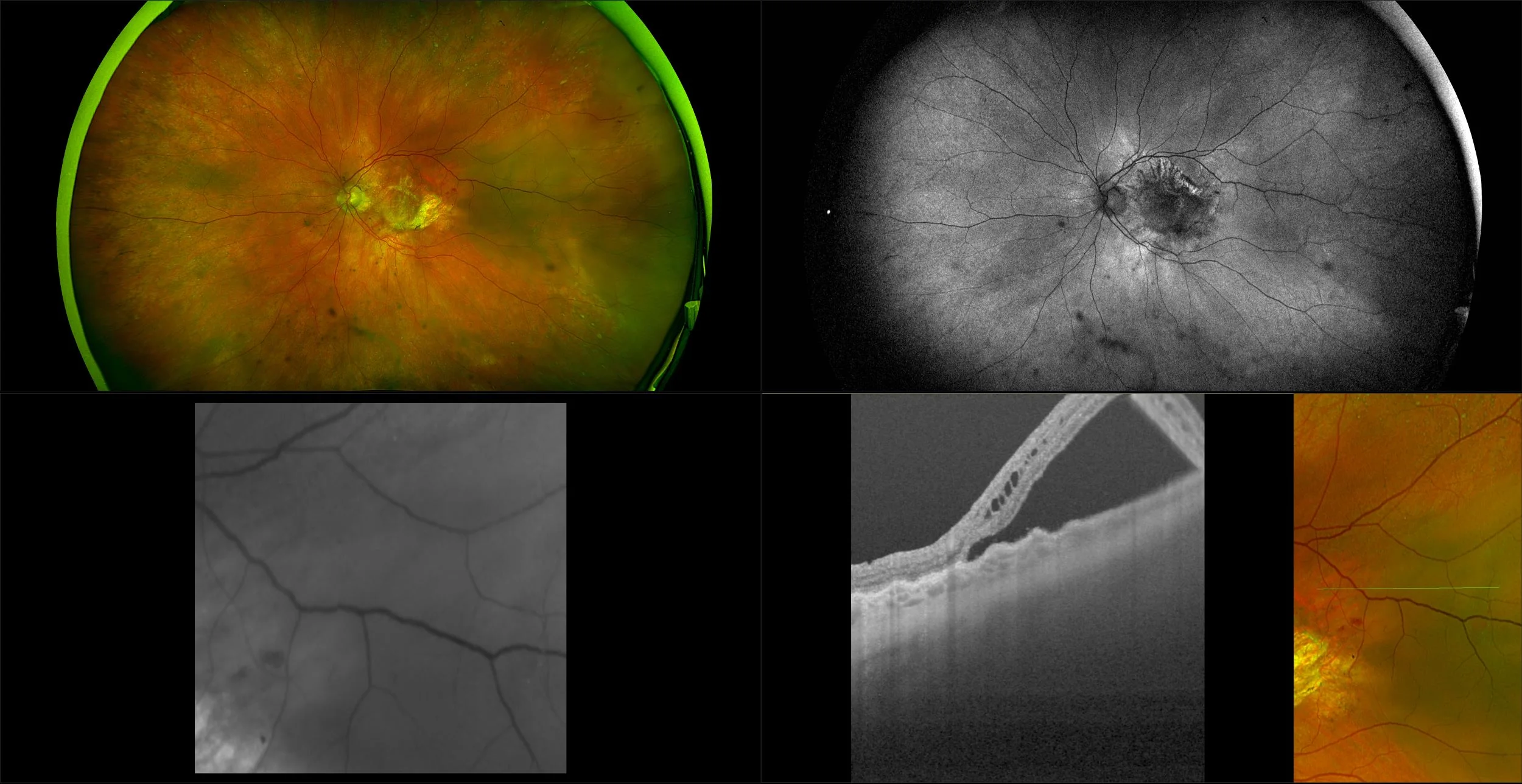
The Normal Distribution of Disc Area on a Combined UWF-SLO + SD-OCT device with Comparison to SD-OCT
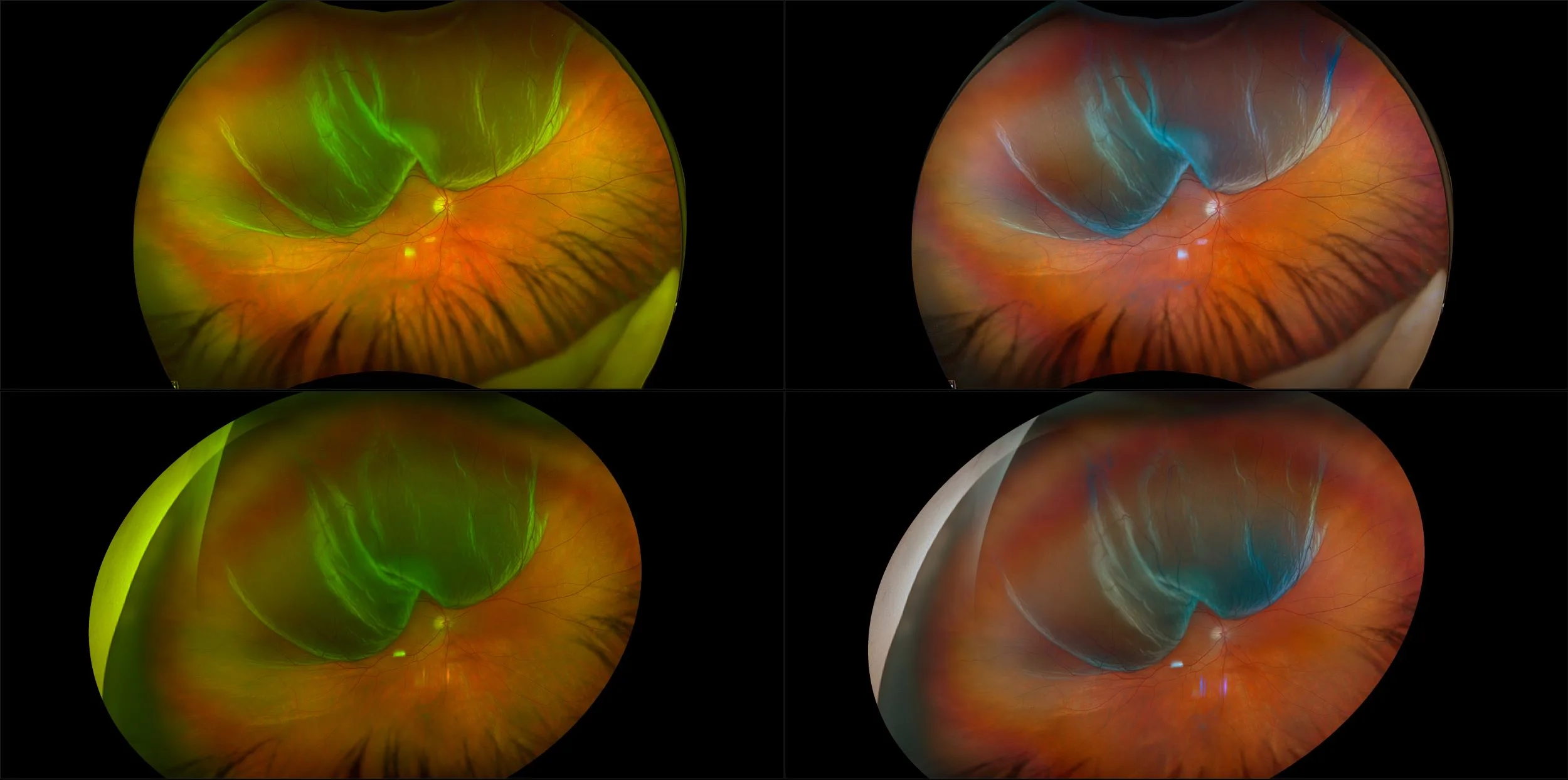
Ultra-Widefield–Guided Swept-Source OCT Findings of Peripheral Vitreoretinal Abnormality in Young Myopes
The thickness changes of retina in high myopia patients during the third trimester of pregnancy: a pilot study